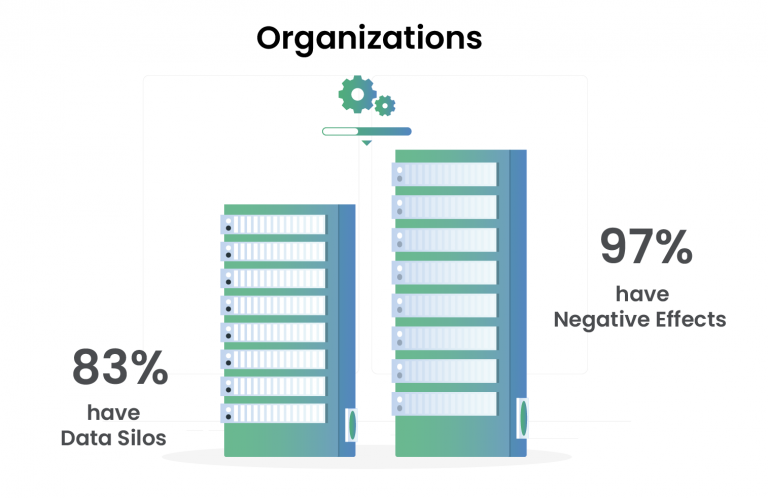
A marketing department of an organization runs its campaigns through an automated marketing tool. The sales department, on the other hand, maintains its customer data in a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform that does not facilitate proper integration with the automated marketing tool. As a result, the marketing outreach data remains isolated within the marketing department, making it difficult to attribute individual sales to a particular marketing campaign. In other words, the marketing and sales departments maintain and manage data silos that pose this typical challenge in most organizations.
A data silo is a repository of data held exclusively by one group and is generally not easily or fully accessible to other groups within the same organization. Siloed data is typically stored in a standalone system, fosters a lack of inclusivity and visibility, and often is incompatible with other data sets.
“35% of enterprise business leaders indicated they have substantial customer data silos across their Organizations.”
The isolated nature of data silos makes it difficult for other factions of the organization to access and use the data, creates barriers to information sharing and collaboration, and hinders business operations and the data analytics initiatives that support them. Although data silos are typically observed in large organizations where business units tend to operate independently and have specific objectives, priorities, and budgets, they can arise in any organization without a sound data management strategy.
Why do data silos exist?
Data silos can have various origins - cultural, organizational or technical. Some of the key reasons for their existence are:
- Lack of vision: Data generated by an external or internal-facing application is consumed by different groups in the organization in different ways. Moreover, teams that directly own data often optimize storage and analytics systems for their primary use cases, and are seldom cognizant of larger, enterprise-wide use cases and objectives that can create additional business value. Consequently, such data can get ‘stuck’ when its full potential value is not realized and only delivers value to a select set of users.
- Technology add-ons to support growth: Usually, organizations start small with simple processes to cater to a limited number of customers. They tend to use easily accessible tools and legacy storage systems. With organic growth, such organizations tend to leverage new technologies to realize fresh opportunities and solve pressing problems, unaware of the data silos being created over time. Inorganic growth (via acquisitions) can also give rise to gaps in data integration between the two entities, further creating silos.
- Organizational structure and management: As enterprises grow and become increasingly vertical in structure, communication and alignment between internal groups/ divisions can tend to devolve, giving rise to skepticism about sharing information/ data with their counterparts. This leads to challenges in maintaining standardized technology infrastructure.
- Use of third-party software applications: Software vendors monetize the data collected by their systems leading to increased data collection cost for enterprises. In most cases, enterprises find it challenging to connect these third-party products with their internal systems, resulting in data silos.
Impact of data silos on organizations
Most enterprises have a unique story of how they came to be shackled by data silos, with large amounts of distinct data that can fully be interconnected, aggregated, and analyzed.
Although the causes for the origin of data silos in each enterprise might differ, the negative effects they have are fairly ubiquitous:
- Wasted resources and low organizational productivity
- High overhead costs due to the storage of the same data in multiple repositories
- Monolithic legacy systems that cause scalability issues and increased licensing costs
- Compatibility issues with ETL tools and increased latency in workflows
- Lack of single source of truth that undermines the quality and credibility of the data and breeds ambiguity
- High search costs to locate the latest data lead to delays in decision making, opportunity loss, and an increase in potential risks
- Inaccurate analysis due to inferior data quality increases the risk of suboptimal decision making, financial planning and budgeting
- Security and access management issues for firms storing sensitive data
Various data analyst houses concur that data silos cause major barriers to the realization of value from data and lead to significant opportunity losses.

Tearing down data silos
Enterprises can seek to secure independence from data silos by implementing a sound data management strategy that ensures data is centralized and optimized for analysis. The market is speckled with many off-the-shelf software solutions that offer cloud-based data lake/ warehouse platforms and claim open-source integrability with prominent ETL/ storage systems. However, a hasty move to adopt platforms that do not necessarily align with the larger business objectives of the enterprise can mean another step toward the “death valley of data swamps”.
Quantiphi has observed that the enterprises that have been successful in attaining freedom from data silos, or are at least on the right track, have predominantly followed the following approach:
- Understand short-term and long-term business needs and strategy
- Identify a use case that can solve a tangible business problem and showcase immediate value (typically a high-value, low-risk use case)
- Integrate all data required to successfully implement the solution in a single, scalable, and secure data platform
- Utilize value created from this implementation to create internal champions and gather leadership support
- Follow these steps iteratively to include other high-value use cases and continue integrating the firm-level data in the platform
Although this approach sounds promising, it’s not nearly a complete one. This strategy poses several challenges - varied data formats and sources, security and compliance issues, gap in adequate skill sets, unavailability of resources to implement the use cases, lack of knowledge on infrastructure decision points and considerations in order to make a decision.
Quantiphi’s invaluable blend of technical and industry expertise in implementing 150+ data modernization projects and successfully migrating over 20 petabytes of data, can help enterprises identify and implement high-value use cases and liberate them from their data silos.
Success Story - Pharmaceuticals & Life Sciences
The customer is a large multinational pharmaceutical and life sciences company. They required assistance in building a long-term system for storing, curating, and sharing medical images and patient healthcare information curated from multiple sources, and leveraged the resultant data lake to develop cutting-edge machine learning and analytics solutions in the healthcare industry.
Problem Context:
The collection and storage of radiology data is often a laborious manual task for organizations with numerous data sources from an unconsolidated infrastructure. Such a process is time-consuming and may fail to uncover insights that have useful business implications. Additionally, organizations that do not have efficient data analytics systems in place experience difficulty in harmonizing multi-source data and running a unified set of analytics across the data sets.
Key Challenges:
- Large datasets
- Incompatibility of ETL tools with custom scripts
- Authentication challenges for pulling and pushing data into a data lake
- Maintaining data integrity
Solution:
Leveraging Google’s HIPAA-compliant products, like Healthcare API, Cloud Dataflow, and BigQuery, Quantiphi built a robust radiology data lake with a customized and integrated DICOM viewer and annotation tool for day-to-day access and analysis. This brought everyday radiology workflows onto a scalable and flexible platform, driving collaboration, growth, and innovation. Consequently, this empowered the organization to unlock vital insights from their radiology data.









Technologies used
Business Impact:
- Improved data quality
- Democratized data for faster and efficient decision-making
- Flexible user management
Get in touch with our experts to liberate your business from data silos.